The landscape of Business Intelligence changes with SQL Server 2012. Microsoft has introduced a new “model” – the BI Semantic Model.
Don’t get too hung up on this word though, the BI Semantic Model is really just an umbrella terminology that says as long as a source follows the BI Semantic Model, it will be supported in the tools. This is the eventual goal anyway; for now there is still a discrepancy which tools support what.
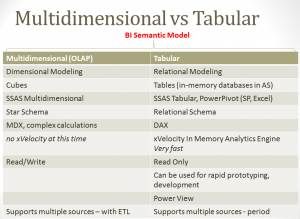
The multidimensional model is the traditional OLAP model. Data source is a cube, that is processed from a data warehouse that usually follows a star schema. Complex calculations and queries using MDX can be done against it. It also allows write-backs.
The new tabular model is not really a “new model” because it is a relational model. Yes the same model we’ve grown accustomed to using when we query our transactional OLTP databases. The difference is, SSAS Tabular is an in-memory database. This is fueled by the xVelocity engine (previously known as Vertipaq), and it also leverages columnstore indexes. All calculations are in memory, and this makes tabular models really fast.
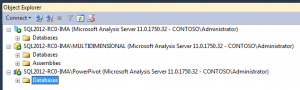
From a UI perspective, if you’re curious, this is what the SSAS engines look like. Notice how the node icons are different:
Here’s a small comparison of Multidimensional vs Tabular:
Fun times ahead!
Additional Resources:
Dustin Ryan’s Creating your First Tabular Model
Simran Jindal’s What is the Business Intelligence Semantic Model Really?
Joshua Fennessy’s MultiDimensional or Tabular – Which Model to Use?








